It is not easy to choose the right partner.
Micronization of Supplements
Problems, Limitations And Errors:
avoiding the common mistakes and getting new customers with new premium products.
Other articles about micronization:
We are experts of in micronization of supplements and micro delivery systems for supplements with high bioavailability.
If you're looking to expand your product's appeal, micronization is the right processes to enlarge your products costumers base. Micronization reduces the particles to a finer size, increases the solubility and the absorption of the active ingredients in your supplement, which will offer more health advantages than ordinary products.
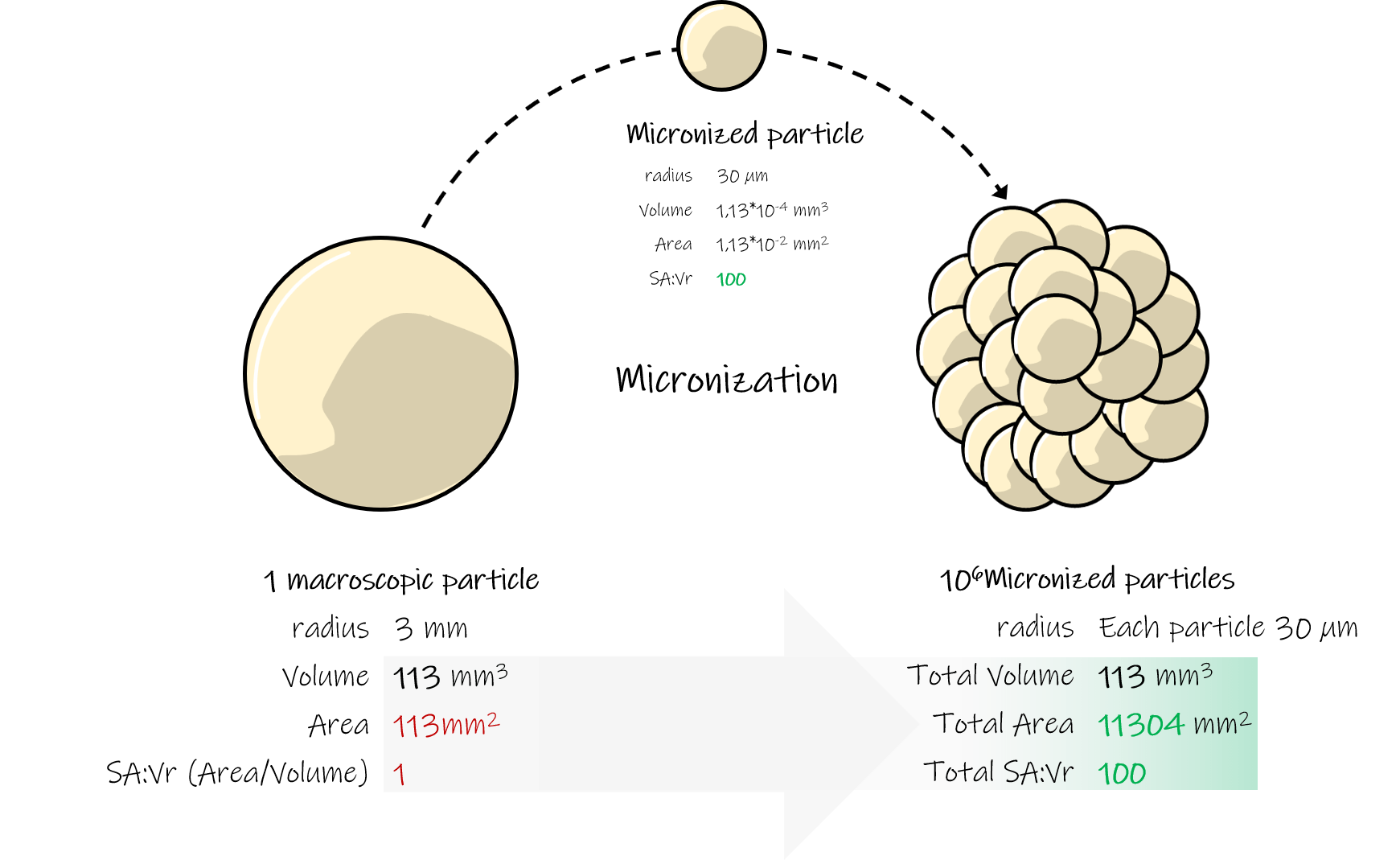
In this article, we'll outline the challenges associated with supplement micronization projects and provide strategies to mitigate them.
What is your micronization goal?
Effective micronization demands a comprehensive understanding of chemistry, pharmaceutical technology, industrialization, and project management. It’s not a singular event but an ongoing process that encompasses formula development, efficacy studies, scale-up, and pilot production. This intricate process necessitates a clearly defined project scope with well-defined objectives. For instance, do you intend to enhance the solubility of poorly water-soluble ingredients in your formulations? Do you seek to augment product stability? Or are you aiming to develop a novel product with advanced controlled-delivery features and enhanced therapeutic efficacy? These distinct micronization goals significantly impact project complexity and its budget.
Micronization a cost or and investment?
Micronization, often perceived as a cost, instead when approached strategically, micronization can translate into a rewarding innovation, enabling the development of superior health products that command a premium market position. By carefully considering the factors influencing costs and implementing effective strategies, companies can maximize the return on their micronization investment. The associated costs span the spectrum from formulation development to commercialization and can be resumed as:
Formulation complexity:
Formulas with numerous components increase the likelihood of compatibility, stability, and technical challenges. This complexity can lead to larger dosage forms difficult to swallow with reduced patient compliance and diminished manufacturing flexibility, preventing the use of the smaller formats unable to contain the whole formulation
Modified release
Formulations incorporating controlled delivery systems, such as gastric protection, enteric delivery, rate-controlled release, and enhanced absorption, incur higher development costs but also impart significant value to the finished product.
Ingredient costs
The choice of premium excipients and active ingredients can significantly impact production costs. Careful selection is essential to balance efficacy, stability, and cost-effectiveness. Consider also how higher bioavailability may lead to effective dose reduction and production cost savings.
Production yields
Achieving high process yields minimizes production costs and enhances profit margins. Optimization of micronization parameters and process control are crucial for maximum yield attainment.
Dedicated marketing campaign
To effectively communicate the unique health advantages of a novel micronized product, a targeted marketing campaign is essential. Scientific data generated during development can be used to support marketing efforts and establish the product’s authority and market trust.
Regulatory Compliance
Micronized supplements adhere to the same regulatory requirements as other supplements, including compliance with ISO 22000 and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) standards. Micronized products are not subject to novel food regulations since their particle size falls within the micron (µ) range (1µm = 1,000 nm). However, it’s worth noting that the EU novel food regulations define nanomaterials as intentionally produced materials with one or more dimensions below 100 nm (Regulation (EU) 2015/2283, article 3, point f). Consequently, it’s crucial to verify that the particle size distribution of your micronization processes does not include any particles with a size of 100 nm or less.
Contractor Audit: Ensuring Quality and Reliability
Before entrusting a contractor with your micronization project, it’s essential to conduct a comprehensive audit to assess their capabilities, track record, and adherence to quality standards. If an in-person audit is not feasible, consider preparing a comprehensive digital questionnaire covering technical expertise, regulatory compliance, safety protocols, and communication practices, and request the prospective contractor to complete it.
The Consequences of Poor Management
Inadequate project design can lead to unrealistic product requirements, while inadequate project management can result in miscommunication, missed deadlines, and strained relationships with stakeholders. These issues can have significant repercussions, including reputational damage, missed market opportunities, and impaired collaboration. To mitigate these risks, dedicate time to early bibliographic research and an IP (intellectual property) anteriority study. The bibliographic research will help establish realistic goals, while the IP study will navigate around potential intellectual property infringements.
How to choose the right micronization provider for you
Micronization providers can be broadly categorized into two main groups: universities/research institutes and private CROs (Contract Research Organizations), each with its distinct strengths and limitations. Academic institutions offer profound expertise in fundamental research and access to state-of-the-art development facilities, making them ideal for handling prototype development and efficacy testing. However, they may lack competencies in commercial-scale production and communication/project management skills. On the other hand, private companies possess expertise in industrial processes and typically offer strong project management capabilities, but may not have the same depth of scientific knowledge. Private companies sometimes compensate their lack of depth in specific areas by subcontracting tasks to academic laboratories, which may lead to higher costs compared to academic institutions.
Two Approaches to Micronization Development:
Multiple contractors
This approach involves hiring multiple contractors to handle specific tasks, such as formula development, efficacy testing, scale-up, and pilot production. This approach grants greater control over each step but demands a higher level of technical understanding of micronization processes and more coordination efforts from your side, as you become the project manager responsible for communication among all contractors.
One contractor development
This approach entails engaging a single provider responsible for the entire project, handling all aspects of micronization from project design to pilot production. This approach liberates you from management and communication duties, potentially leading to faster project execution and a more cohesive product development strategy.
How to choose the right approach for you
The choice between multiple contractors and one contractor development depends on your specific needs, resources, and level of expertise. If you have a deep understanding of micronization processes, require meticulous control over each step, and have the man-hours to dedicate to the management of the whole micronization project, the multiple contractor approach may be suitable. However, if you prefer a streamlined process with a single point of contact and are less concerned with granular control or just do not have the competencies and/or the man-hours one contractor development may be more efficient.
Conclusion
Micronization increase the value of your products, it enhances the efficacy and bioavailability of your supplements making them a better option than competitors’ products. However, it’s important to carefully consider the challenges and choose the right approach. If you have the time and the scientific background suitable to actively manage the processes you could consider to directly manage the project. Differently you should hire a single partner executing al the activities for you. Regarding the costs is hard to say which options is the most cost effective since the responsibility of the project management will come with a premium price which could ideally counterbalanced by resource optimization if the company in charge has the capability to execute all the activity in-house. You should also account that having someone else managing the whole project it free up time you can dedicate to other projects or task in your company. On the opposite end of the spectrum if you directly manage the project and contract only academic laboratories for all the activities you could experience a substantial money saving and access to state-of-the-art knowledge and facilities, but you should also account for the extra resources to manage directly the micronization project and assess the adequacy of your scientific competencies to direct and communicate with the several experts involved in the micronization of your product.
Technology Scientific is the SME born as an
academic spin-off
our innovation services are used by
top companies and startups






FREE PDF GUIDE
The Complete Guide to
craft a successful innovation plan for supplement micronization
The ultimate and free guide to easily design an innovation project for supplement micronization, proven to increase the bioavailability and efficacy of your products.
With Technology Scientific in vitro permeation studies,

